Introduction
Turning a small operation into a large enterprise requires strategy, discipline, and the right mix of execution and adaptation. This guide explains how to grow a small business into a large business with actionable steps, frameworks you can apply immediately, and answers to common concerns.
- Key metrics to track for scalable growth
- Systems and processes to reduce friction
- Marketing and sales strategies that scale
- Hiring, culture, and leadership essentials
- Financing, partnerships, and risk management
Key Takeaways and Next Steps
Recap of the growth blueprint
To grow a small business into a large business: clarify a measurable vision, build repeatable systems, focus marketing on high-value segments, create predictable sales and pricing, hire leaders, manage cash, and use data to iterate.
Immediate actions you can take today
1) Run a 30-day audit of unit economics. 2) Document one critical SOP. 3) Launch one measurable acquisition experiment. 4) Build a simple 12-month cash forecast.
Longer-term priorities
Invest in leadership hires, scalable technology, and a culture that supports learning. Reassess strategy quarterly and remain disciplined about not scaling before fundamentals are proven.
Define a Scalable Vision: Foundation for How to Grow a Small Business into a Large Business
Craft a clear, measurable growth vision
Start by writing a concise growth vision: target revenue, customer segments, geographic reach, and timeline. For example, “Grow from $500k to $10M in five years by expanding into two new regions and increasing average order value by 30%.” Measurable targets guide resource allocation and decision-making.
Align mission, values, and long-term goals
Large businesses with sustainable growth have aligned purpose and values. Document your mission and ensure product, customer service, and hiring align with it. This alignment helps maintain consistency as the organization scales.
Set OKRs and KPIs that drive execution
Adopt Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) and define KPIs for revenue, retention, CAC, LTV, churn, conversion rates, and gross margin. Review these weekly or monthly to spot trends early and adjust tactics.
Build Repeatable Systems and Processes
Standardize core processes for efficiency
Map customer journey steps, sales workflows, supply chain, and fulfillment. Create standard operating procedures (SOPs) for recurring tasks. Documenting processes reduces errors and training time as you hire more people.
Automate repetitive tasks and workflows
Identify tasks that can be automated: invoicing, email follow-ups, inventory alerts, payroll, and marketing campaigns. Use affordable tools and integrate them through APIs or middleware to eliminate manual handoffs.
Measure process performance and iterate
Track time-to-complete, error rates, cost per transaction, and throughput. Use these metrics to prioritize improvements that increase capacity without proportional cost increases- essential to scale profitably.
Market Strategically: How to Grow a Small Business into a Large Business with Demand Generation
Identify high-value customer segments
Analyze existing customers to determine which segments deliver the highest lifetime value and lowest acquisition cost. Prioritize marketing spend on these segments to maximize ROI and accelerate growth.
Create a multi-channel acquisition plan
Combine inbound (content, SEO, organic social) and outbound (paid ads, partnerships, events). Test channels, measure CAC by channel, and double down on those with repeatable performance. Use a 70/20/10 budget split: scale winners, optimize promising channels, and experiment.
Optimize conversion funnels continuously
Map the conversion funnel from awareness to purchase. Run A/B tests on landing pages, offers, and messaging. Improve micro-conversions (email signups, product demos) to increase pipeline volume without increasing spend linearly.
Sales and Revenue Operations for Scalable Growth
Build a predictable sales process
Define stages, qualification criteria, average deal size, and sales cycle length. Equip sales reps with playbooks and templates. Predictability in sales enables forecasting and capacity planning essential when scaling.
Invest in CRM and sales enablement
Implement a CRM to centralize pipeline data and enable performance tracking. Use automation for lead routing, follow-up reminders, and reporting. Provide sales enablement content such as pitch decks, objection handling, and case studies.
Price for scale and profitability
Review pricing strategies to balance market competitiveness and margins. Consider tiered pricing, volume discounts, and value-based pricing that can increase average revenue per customer as you scale.
People, Culture, and Leadership to Support Expansion
Hire for key roles and leadership capacity
Identify roles that unlock growth: head of sales, head of marketing, operations lead, and finance/controller. Hire leaders who can build teams and processes, not just individual contributors.
Create a scalable organizational structure
Design reporting lines and team boundaries that support collaboration and accountability. Use small cross-functional teams with clear owners for product, growth, and customer success to reduce bottlenecks.
Foster culture and retention as you expand
Scale culture intentionally: document norms, celebrate wins, provide transparent communication, and invest in development. High retention reduces hiring costs and preserves institutional knowledge during rapid growth.
Finance, Funding, and Risk Management
Prepare financial models and scenario planning
Develop a three-way financial model (income statement, balance sheet, cash flow) with base, optimistic, and conservative scenarios. Model the cash needs for scaling hires, marketing, and inventory to avoid surprises.
Choose the right funding path
Consider self-funding, bank loans, venture capital, or strategic partnerships. Choose based on growth speed, control preferences, and capital needs. For example, VC can accelerate growth but dilutes ownership and adds investor expectations.
Manage risk and compliance proactively
As you grow, legal, tax, and regulatory risks increase. Implement basic governance—contracts, insurance, IP protections, and accounting controls- to avoid costly setbacks that can derail scaling efforts.
Product and Service Expansion Strategies
Improve core offering before expansion
Perfect the core product for reliability, customer satisfaction, and defensibility before adding new lines or markets. Customer feedback loops and NPS are critical inputs for product readiness.
Expand thoughtfully: horizontal vs. vertical moves
Decide whether to expand horizontally (new products for same customers) or vertically (enter new customer segments). Evaluate synergies, distribution channels, and incremental costs for each option.
Use pilots and phased rollouts
Run small pilots in new markets or with new products to validate demand and refine operations. Use phased rollouts to spread financial and operational risk while collecting data for full-scale launches.
Technology and Data: Scale with Smarter Systems
Invest in scalable tech stack
Choose cloud-based, modular systems for ERP, CRM, e-commerce, and analytics. Scalable platforms reduce rework and integration costs as transaction volumes grow.
Leverage data for decision-making
Centralize data into dashboards for sales, marketing, operations, and finance. Use cohort analysis, churn prediction, and LTV models to prioritize initiatives with the highest growth leverage.
Use AI and automation to gain efficiency
Apply AI for customer support triage, lead scoring, demand forecasting, and personalization. Automating repetitive decisions frees human talent to focus on strategy and complex problem-solving.
Operational Scaling: Supply Chain, Fulfillment, and Customer Success
Strengthen supply chain resilience
Diversify suppliers, build safety stock, and negotiate flexible terms. Use demand forecasting to align procurement and reduce stockouts or excess inventory as order volume grows.
Scale fulfillment and distribution
Assess whether in-house fulfillment or third-party logistics (3PL) best supports scale. 3PL partners can provide capacity and geographic reach quickly while you focus on core business.
Prioritize customer success to reduce churn
Invest in onboarding, proactive outreach, and education. High touch in early lifecycle and automated nurturing later can increase retention rates, which compound revenue growth significantly.
Measure, Learn, and Iterate Continuously
Adopt a test-and-learn culture
Run structured experiments with clear hypotheses, metrics, and timelines. Use results to scale winners and kill underperformers. Systematic learning shortens time to product-market fit in new initiatives.
Use leading indicators to spot issues early
Track leading metrics like trial-to-paid conversion, support ticket volume, and on-time delivery rates. These indicators let you act before lagging indicators like revenue decline.
Regularly reassess strategy and pivot when needed
Quarterly strategy reviews aligned with data help you pivot resources. Be willing to change market focus, pricing, or distribution if evidence indicates better paths to scale.
How to Grow a Small Business into a Large Business: Actionable First 90 Days Plan
Day 1–30: Diagnose and prioritize
Audit finances, customer metrics, and operations. Create a prioritized list of high-impact changes: top 3 process fixes, top 3 customer segments to pursue, and 3 quick marketing experiments.
Day 31–60: Implement systems and hire
Document SOPs for high-priority processes, implement essential tools (CRM, accounting, analytics), and hire 1–2 critical roles to increase capacity- preferably sales or operations leaders.
Day 61–90: Test growth engines and scale what’s working
Run controlled experiments on acquisition channels and pricing. If experiments hit target KPIs (CAC payback, conversion lift), reallocate budget to scale winners rapidly.
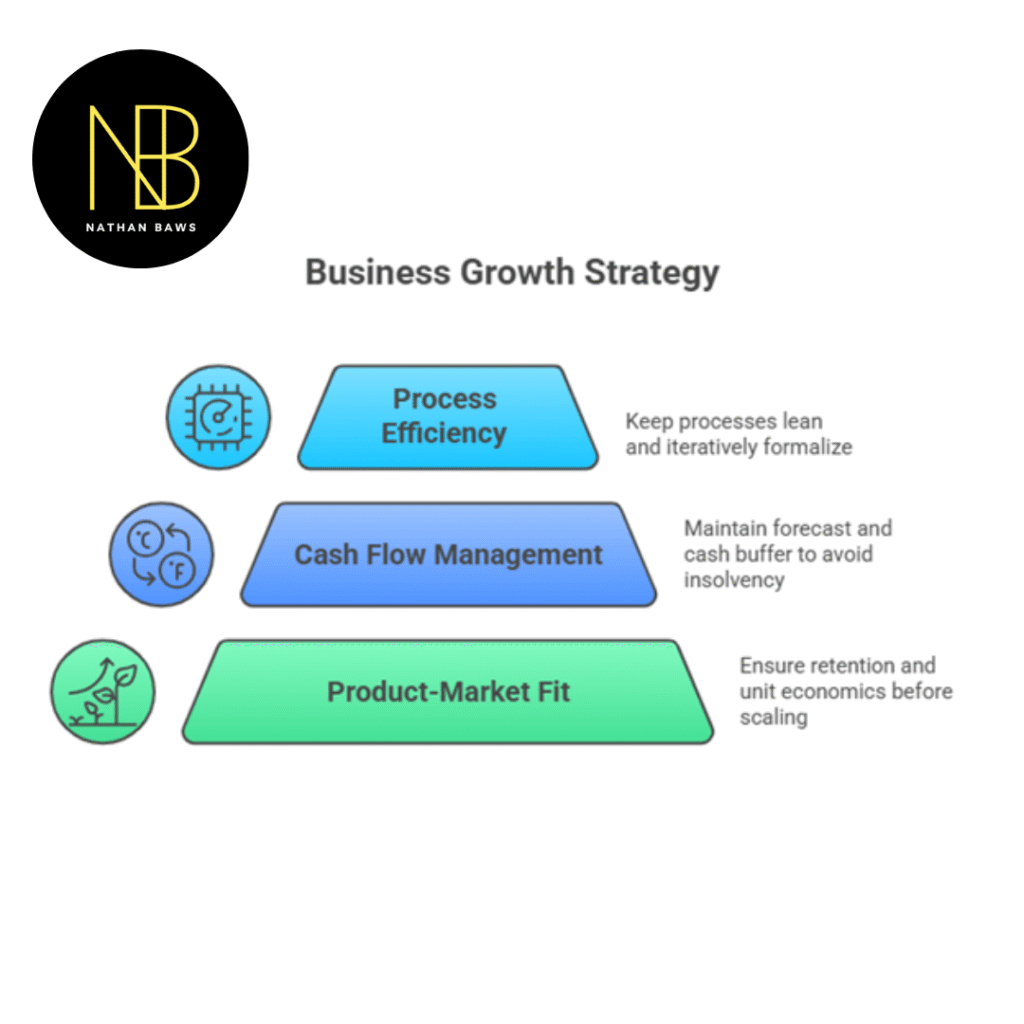
How to Grow a Small Business into a Large Business: Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Growing before product-market fit
Avoid aggressive scaling until retention and unit economics are proven. Premature scaling wastes capital and obscures root issues with acquisition or product design.
Neglecting cash flow management
Maintain a rolling 12-month cash forecast and a minimum operating cash buffer. Fast revenue growth can still lead to insolvency if receivables and inventory outpace cash inflows.
Overcomplicating processes too early
Keep processes lean and iteratively formalize them. Over-engineering slows adaptability; document what matters and continue improving based on data.
Conclusion
Following these structured steps and focusing on measurable, repeatable improvements will increase your odds of successfully growing your small business into a large business. Start with clarity, measure relentlessly, and scale systems and people in alignment with proven unit economics.
10 FAQs: How to Grow a Small Business into a Large Business
1. How long does it take to grow a small business into a large business?
There is no fixed timeline. Many factors- market size, product-market fit, capital, and team—affect pace. Typical fast-growth cases take 3–7 years, while steady scale may take 7–15 years.
2. What is the single most important factor to scale?
Repeatable unit economics (positive contribution margin and payback period) are critical. If each customer adds profitably over time, scaling becomes financially feasible.
3. Should I raise capital to grow faster?
Only if capital accelerates validated growth paths that maintain margins. Avoid taking funding that compels unsustainable growth if unit economics aren’t proven.
4. How many employees do I need before scaling?
There is no magic number. Focus on hiring key roles that unblock growth- sales, ops, finance—and scale the headcount matched to demand and processes.
5. How important is company culture when scaling?
Very important. Culture preserves decision-making norms and productivity during rapid growth. Invest in communication, values, and leadership development early.
6. What metrics should I track weekly?
Track revenue, gross margin, CAC, LTV, churn, conversion rates, and cash balance. Weekly visibility enables quicker corrective actions.
7. When should I expand into new markets?
Expand after proving your model in the initial market, optimizing unit economics, and ensuring operations can support incremental volume. Use pilots to validate demand in new markets.
8. How do I keep customer service high while scaling?
Combine automation for routine tasks with dedicated human support for complex issues. Invest in onboarding and proactive support to prevent escalation and improve retention.
9. How can I scale without losing control of quality?
Use SOPs, quality KPIs, frequent audits, and a culture that empowers frontline employees to escalate issues. Quality gates in processes prevent defects from multiplying.
10. What are low-cost ways to increase growth early on?
Focus on referrals, partnerships, content marketing, and improving conversion rates. Optimizing current channels often yields higher ROI than launching new paid campaigns.
Also Read: 10 Unorthodox Growth Hacks That Helped Me Thrive After Shark Tank


